Interlock Ransomware Group Delivers Malware Using New 'FileFix' Technique

The ransomware group Interlock is deploying a Remote Access Trojan (RAT) via compromised websites, using a novel social engineering method known as FileFix for malware delivery.
ClickFix Attacks: A Growing Threat
FileFix is a variant of the broader ClickFix attack technique, which leverages social engineering to trick victims into infecting their own systems. These attacks have surged by 517% between late 2024 and mid-2025, according to researchers at ESET.
ClickFix attacks typically direct users to fake websites, where they are misled into copying and executing malicious PowerShell commands. These commands are often disguised as browser fixes or requirements to pass fraudulent CAPTCHA challenges.
While Windows users are the primary targets, ClickFix campaigns have also been observed targeting macOS and Linux systems.
How FileFix Works
Recently documented by security researcher mr.d0x, FileFix refines the ClickFix method by exploiting Windows File Explorer rather than relying solely on command-line interaction.
The attack flow is as follows:
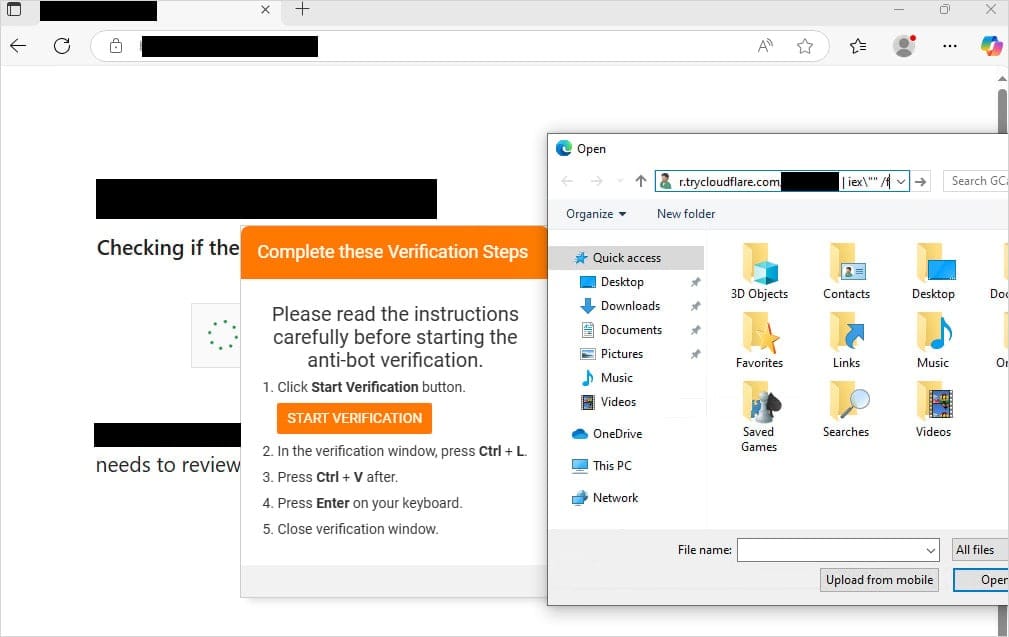
- Fake File Share Lure – A phishing page claims the victim has been granted access to a shared file.
- “Open File Explorer” Button – Clicking the button launches File Explorer and silently copies a malicious PowerShell command to the clipboard.
- Manual Execution – When the victim pastes the path and hits Enter, the command runs—deploying the Interlock RAT.
Interlock RAT Deployment & Capabilities
In May 2025, researchers from The DFIR Report and Proofpoint identified Interlock RAT being distributed via KongTuke (also known as LandUpdate808), a Traffic Distribution System (TDS) that utilizes ClickFix tactics, including fake CAPTCHA pages, to launch multi-stage malware infections.
By early June 2025, attackers pivoted to the FileFix method. Depending on the campaign, they delivered:
- A PHP-based version of Interlock RAT
- In some cases, a Node.js variant of the malware
Once deployed, the RAT executes the following:
- Gathers system information via PowerShell
- Checks for administrative privileges
- Establishes persistence on the host system
- Enables interactive control by attackers, including:
- Searching for backup files
- Exploring directories
- Probing domain controllers
- Uses RDP for lateral movement within networks
To evade detection, the malware routes command-and-control (C2) traffic through Cloudflare Tunnel, using trycloudflare.com to mask communications.
Opportunistic Campaign
Researchers at The DFIR Report describe this as an opportunistic campaign, targeting victims through compromised websites rather than highly tailored spear-phishing efforts.
This marks the first publicly documented use of FileFix in live attacks, highlighting the increasing sophistication of ransomware groups in exploiting everyday user behaviors.
Mitigation Recommendations
- Never copy-paste commands from unknown or suspicious websites.
- Disable automatic PowerShell execution in untrusted contexts.
- Monitor for unusual RDP activity or unexplained use of Cloudflare Tunnel.
- Update endpoint protection tools to detect FileFix and ClickFix techniques.
Interlock’s shift to FileFix underscores a troubling trend—attackers continuously evolving social engineering tactics to bypass user awareness and technical defenses.
Stay vigilant. Even a single click can open the door.